Welcome back to this mini blog series on teaching the 8 Standards of Mathematical Practices! In this series, I have been discussing how you can encourage these math habits with your students. If you missed the previous posts, you can check them out here and here. Today, I will be going over Standard of Mathematical Practice 5 and 6. So, let’s get started on learning about math tools and being precise in math!

Imagine if you were asked to build a treehouse for your school playground. Would you know where to begin? I would imagine you would need certain tools such as a cordless drill, nail gun, and saw. You would also have to know precise vocabulary terms such as galvanized joist hangers, deck screws, washers, etc. In math, students may not be asked to build treehouses, but they are asked to complete math tasks and solve problems. They need to be able to access math tools and use precision in order to solve problems. Math Practices 5 and 6 help with both of these things.
Teaching The Standard for Mathematical Practice
Math Practice 5: Use Appropriate Tools Strategically
In this math practice, students strategically choose math tools to help them complete a task. The math tools may be conventional items such as a ruler or unconventional items such as using paperclips to measure an object. Math tools usually fall into five categories: supplies, manipulatives, representational tools, digital tools, and mental math tools.
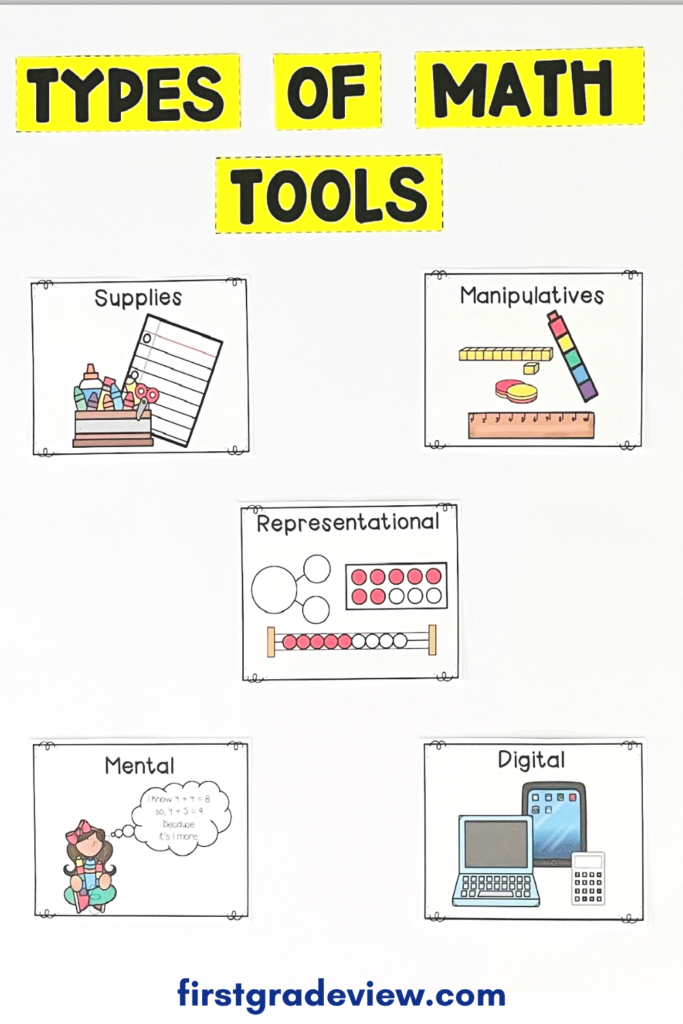
Supplies- Supplies include all the items students may use to record, draw, measure, or create as they complete a math task. Materials such as paper, a pencil, whiteboard, etc. would fall under the supply category.
Manipulatives– Manipulatives include all the physical objects that students can touch when working on a math task. Unifix cubes, pattern blocks, counting bears, and base ten blocks are examples of math manipulatives.
Representational Tools– Representational tools help students see structure of numbers and can be used when solving math problems. They usually serve as a type of graphic organizer. Ten frames, number bonds, number lines, and 120 charts are all considered representational tools.
Digital Tools– Digital tools are technology based math tools that help students solve a math problem. Digital tools can be virtual manipulatives or representational tools such as a number line. Apps that allow students to work on math are also considered digital tools.
Mental Math Tools– Mental math tools are the strategies or approaches students take when solving a math task. These strategies serve as a mental toolbox for students. Counting, estimating, using place value, decomposing and composing numbers, and using derived facts are all examples of mental math tools.
Activities to Build the Standard of Mathematical Practice 5
Now that you know the different types of math tools, you may be wondering, “How do I reinforce this math practice with my students?” The following activities are examples of how students can build math habit 5.
Counting Collections– In this activity, students count a set of items predetermined by the teacher. You would predetermine the number of items in each set based on the needs of your class. Students could work alone, with a partner, or a small group to count their items. Graphic organizers such as ten frames and 100 charts or supplies such as small cups could be provided to students to help them organize their count. Remember, it is important that students decide on how they want to organize their count. Afterwards, students would record and share their strategies for how they conducted their count.

Anchor Charts– You can create an anchor chart of math tools that students can use when solving problems. The charts could be specific to certain math tasks such as “Our Measuring Tools” or “Our Math Strategies for Counting On.”
Math Talks– Math talks are a great way to get your class to discuss why they chose certain math tools and how they used them. These discussions will not only help your students develop this math practice, but also support their thinking about their intention when selecting math tools.
Questions to Build Math Practice 5
You can use the following questions with any math task to help develop Math Practice 5 with your students.
- What math tools can you use to represent the problem?
- What estimate did you make for the answer?
- What can using a _____ show us that _______ may not?
- For this problem, would it be helpful to use a graph…number line…ruler…drawing…ten frame…base ten blocks?

Math Practice 6: Attend to Precision
In this math practice, students need to understand that math is not just about getting the right answer. Mathematically proficient students can also clearly communicate their thinking in addition to finding the answer. This math practice allows students to develop their math vocabulary by having them explicitly describe their thinking, justification, and reasoning. Math Practice 6 also takes into account the importance of students' understanding of math symbols.
Activities to build the Standard of Mathematical Practice 6
The following activities are examples of how students can build this math habit.
Mystery Rule– In this activity, students are shown a set of numbers or images. The numbers or images are then sorted into either “follow the rule” or “does not follow the rule.” Students must then decide what the category or rule is based on deductive reasoning.

Encourage Labeling– When students are working on math word problems, encourage them to include a label as part of their solution. You can also encourage students to use labels when showing their math strategies such as labeling their counting or labeling number bonds. Explain that being precise is a part of Math Practice 6.
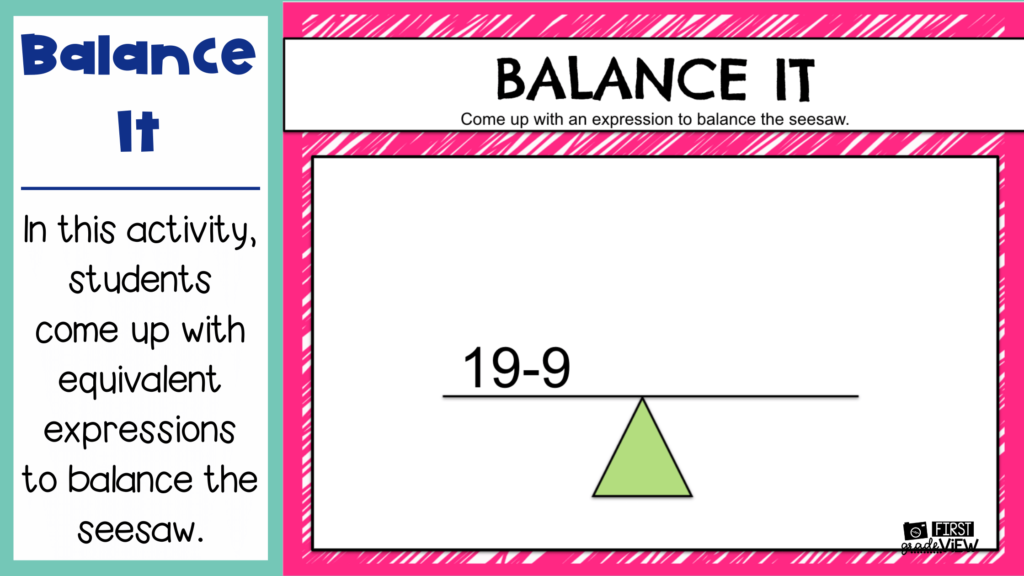
Balance It- For this activity, present students with a number or expression. Explain that they must keep the seesaw balanced by including a number or expression for the other side that is equivalent.
Questions to Develop Math Practice 6
- How do you know your answer makes sense?
- Is there a more efficient strategy you could have used?
- How are you showing the meaning of the quantities?
- How can you check your work and test your solution?

I hope this blog post helps you get some ideas of how you can easily incorporate the 8 Standards of Math Practice into your classroom. Check out these math practice posters for your classroom! Be sure to come back as I will be wrapping up this series with Math Practices 7 and 8!
You may also like:
Teaching the 8 Standards of Math Practice: Math Practice 1 and 2
Teaching the 8 Standards of Math Practice: Math Practice 3 and 4








No Comments